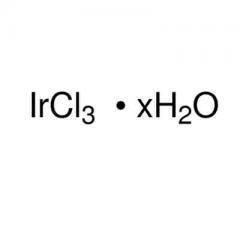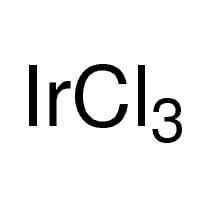Iridium
| Identification | ||
| Name |
|
iridium |
| Synonyms |
|
IRIDIUM ON ACTIVATED CARBON; IRIDIUM ON ALUMINA IRIDIUM POWDER; IRIDIUM SPONGE; IRIDIUM BLACK; IRIDIUM METAL; IRIDIUM PELLET; |
| Molecular Formula |
|
Ir |
| Molecular Weight |
|
192.22 |
| CAS Registry Number |
|
7439-88-5 |
|
EINECS |
|
231-095-9 |
| Properties | ||
| Melting point |
|
2443 ºC |
| Boiling point |
|
4500 ºC |
|
Water solubility |
|
INSOLUBLE |
|
Density |
|
1.05 g/mL at 25 °C |
|
Storage conditions |
|
Flammables area |
|
Appearance |
|
Grey powder |
|
Iridium content |
|
Original Ir Purity 99.95% |
|
Package |
|
5g,100g,1kg/bottle (according to customer requirements) |
| Safety Data | ||
| Hazard Symbols |
|
Xi |
|
Risk Codes |
|
R36/37/38 |
|
Safety Description |
|
S26 |
|
Transport Information |
|
UN 1789 |
|
Customs code |
|
28439000 |
Iridium Usage and Synthesis Method:
The earliest application of iridium was as a pen tip material, and later it was used in injection needles, balance blades, compass supports, electrical contacts, and so on.The iridium crucible can be used to grow refractory oxide crystals. The crucible can work at 2100-2200°C for several thousand hours and is an important precious metal vessel material.
The high-temperature oxidation resistance and thermoelectric properties of iridium make the iridium/iridium-rhodium thermocouple the only precious metal temperature measurement material that can measure the volume in the atmosphere up to 2100℃; it can be used as a container material for radioactive heat sources; anodized iridium film is one A promising electrochromic material.Ir192 is a gamma-ray source, which can be used for non-destructive testing and radiochemotherapy.At the same time, iridium is a very important alloying element, and some iridium alloys are used in some key sectors; iridium compounds also have their own unique uses.
Preparation:
Iridium is a by-product of nickel and copper mining and refining processes. During the electrolytic refining of nickel and copper, precious metals such as gold and silver, platinum-based elements, and non-metallic elements such as selenium and tellurium will accumulate on the positive electrode. This mud-like substance must enter the solution to separate the metal from it. The specific method depends on the composition of the mixture, but there are two main ones: dissolve in aqua regia after adding sodium peroxide, or directly dissolve in a mixed solution of chlorine and hydrochloric acid.
Safety:
Agglomerated iridium metal has no biological use and is harmless because it does not react with biological tissues. Like most metals, fine metal powders of iridium are dangerous. Such powder can irritate tissues and burn easily in the air. Since the treatment volume of iridium compounds is generally very low, little is known about its toxicity. However, soluble salts of iridium, such as various iridium halides, are toxic. Most iridium compounds are insoluble, so it is difficult to be absorbed by the body. Ir isotopes are as dangerous as other radioactive isotopes. The only related accident was accidental exposure to this isotope during brachytherapy. The high-energy gamma rays emitted by Ir will increase the possibility of cancer. External exposure can cause burns, radiation poisoning and even death. Ingestion of Ir can cause burns to the gastrointestinal lining. Ir, Ir, and Ir that enter the body are mainly accumulated in the liver, and the gamma rays and beta radiation emitted can cause damage to the body.