| Identification | ||
| Name |
|
Hydroxypropyl acrylate |
| Synonyms |
|
Acrylic acid propane-1,2-diol ester; hydroxypropyl acrylate, mixture of isomers; 1,2(or3)-propanediol,1-acrylate; propyleneglycolacrylate; acrylicacid,2-hydroxypropylester; |

|
||
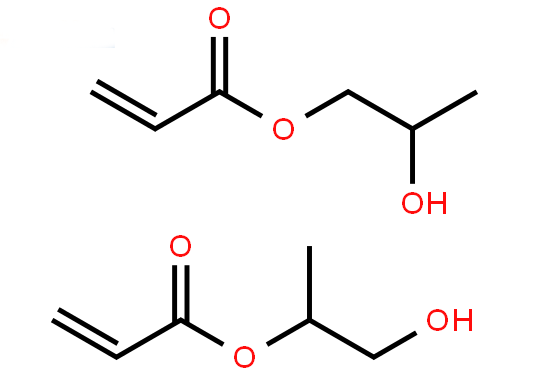
| Molecular Structure |
|
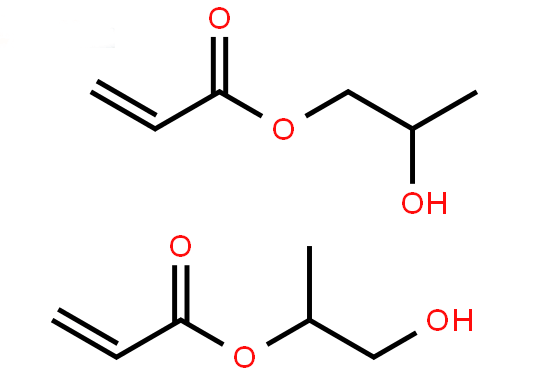 |
|
|
||
| Molecular Formula |
|
C6H10O3 |
| Molecular Weight |
|
130.14 |
| CAS Registry Number |
|
25584-83-2 (91313-64-3) |
| Properties | ||
| Density |
|
1.044 |
| Boiling point |
|
77 ºC (5 mmHg) |
|
Melting point |
|
-92°C |
| Refractive index |
|
1.445 |
| Flash point |
|
193 ºF |
| Vapor density |
|
4.5 |
| Safety Data | ||
| Hazard Symbols |
|
T |
| Risk Codes |
|
R23/24/25;R34;R43 |
| Safety Description |
|
S26;S36/37/39;S45 |
| Transport Information |
|
UN 1760 |
Uses of hydroxypropyl acrylate:
It can be used to produce adhesives, thermosetting coatings, fiber treatment agents and synthetic resin copolymer modifiers, and can also be used to prepare lubricant additives.
It can be used to produce thermosetting coatings, adhesives, fiber treatment agents and modifiers for synthetic resin copolymers. It can also be used as one of the main crosslinkable functional group monomers used in acrylic resins.
Mainly used in the manufacture of thermosetting acrylic coatings, light curing coatings, photosensitive coatings, textile treatment agents, adhesives, paper processing, water quality stabilizers and polymer materials. It has the characteristics of low usage, but can significantly improve the performance of the product.
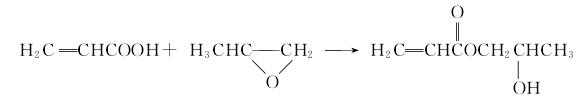
Production method of hydroxypropyl acrylate:
Acrylic acid is prepared by oxidation of propylene or hydrolysis of acrylonitrile. Acrylic acid and propylene oxide are then subjected to an addition reaction under the action of a catalyst and iron, aluminum, chromium and other polymerization inhibitors to produce a crude product of 2-hydroxypropyl acrylate, which is degassed and rectified to obtain a finished product. The main reaction is as follows: