| Identification | ||
| Name |
|
Benzylidene-bis(tricyclohexylphosphine)dichlororuthenium |
| Synonyms |
|
Bis(tricyclohexylphosphine) benzylidine ruthenium(IV) chloride Phenylmethylenebis(tricyclohexlPhosPhine)ruthenium chloride Bis-(tricyclohexylphosphine)-benzylideneruthenium Bis(tricyclohexylphosphine)benzylidine ruthenium(lV) dichloride Grubbs (1st generation) |

|
||
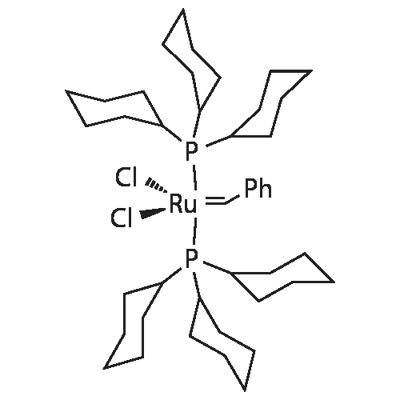
| Molecular Structure |
|
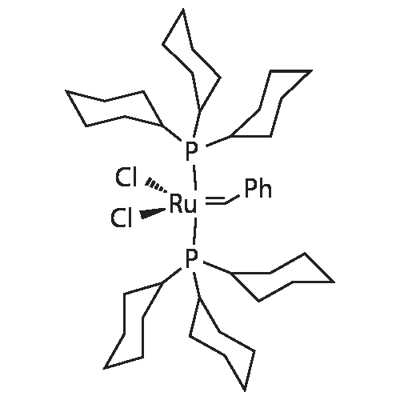 |
|
|
||
| Molecular Formula |
|
C43H72Cl2P2Ru |
| Molecular Weight |
|
822.96 |
| CAS Registry Number |
|
172222-30-9 |
| Properties | ||
| Melting point |
|
153 ºC (dec.) |
|
Storage conditions |
|
2-8°C |
| Safety Data | ||
| Hazard Symbols |
|
Xi |
| Risk Codes |
|
R36/37/38 |
| Safety Description |
|
S26;S36 |
Benzylidene-bis(tricyclohexylphosphine)dichlororuthenium application:
Benzylidene-bis(tricyclohexylphosphine)dichlororuthenium can be widely used in organic synthesis as the first metathesis catalyst; under a wide range of reaction conditions, it can be effectively used in the tensioned ring-opening metathesis polymerization of end-olefin olefins. Reaction, olefin cross metathesis and ring-closure metathesis unit and vinyl alcohol decomposition reaction of internal olefin. Phenylmethylene bis(tricyclohexylphosphorus) ruthenium dichloride is a new type of arylalkylidene-ruthenium complexes (arylalkylidene-ruthenium complexes), which can be used as a catalyst in metathesis reactions.
Benzylidene-bis(tricyclohexylphosphine)dichlororuthenium preparation:
The preparation of phenylmethylene bis(tricyclohexylphosphorus) ruthenium dichloride is as follows:
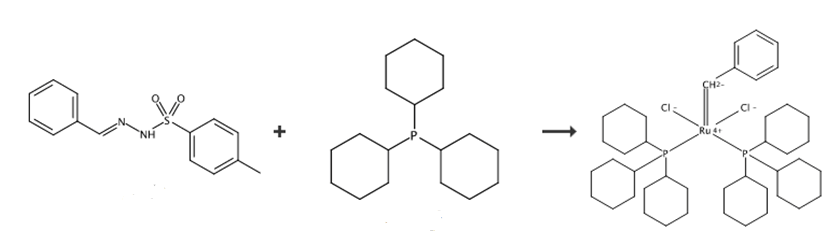
1) Add 4.96 grams of benzaldehyde-p-toluenesulfonyl hydrazone, 1.75 grams of sodium methoxide and 40mL of The triethylene glycol was placed in a 60°C water bath for the synthesis reaction for 1 hour. After the synthesis reaction is completed, the methanol in the obtained synthesis reaction solution is extracted with a water pump to obtain a synthesis reaction product; the synthesis reaction product is extracted with n-pentane in ice water and then extracted with a saturated aqueous NaCl solution. The obtained extraction product was spin-dried to obtain phenyldiazomethane; the yield of the phenyldiazomethane was 50%.
2) Add 4.0 grams of dichlorotris(triphenylphosphine) ruthenium to a 250mL vial, and pass nitrogen gas to replace the air in the vial, and inject 40mL into the vial. Nitrogen freeze-thaw treated dichloromethane; place the vial in a cold bath at -78°C, and add the pentane of phenyldiazomethane with a mass concentration of 98.5mg/mL at -50°C under stirring conditions Mix 10 mL of alkane solution. The phenyl diazomethane in the pentane solution of phenyldiazomethane is the phenyldiazomethane prepared above; the resulting mixture is stirred at -70°C for 10 minutes and then 40mL,- A dichloromethane solution of tricyclohexylphosphine with a mass concentration of 0.064 g/mL at 50°C was reacted at 25°C for 30 minutes. After the reaction is over, the resulting reaction solution is filtered to remove insolubles, the filtered reaction solution is concentrated to 10 mL and then filtered again, and 100 mL of methanol that has undergone three liquid nitrogen freeze-thaw treatments is added to the resulting filtered product for precipitation , The obtained precipitate was washed three times with methanol and then twice with acetone, and the washed precipitate was vacuum dried for 3 hours to obtain 2.1 g of product. The yield of the product prepared by the method provided in Example 2 of the present invention is 81%. The product obtained above is subjected to proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum and phosphorus spectrum detection, and the detection result is that the product obtained is phenylmethylene bis(tricyclohexylphosphorus) ruthenium dichloride.
Benzylidene-bis(tricyclohexylphosphine)dichlororuthenium uses:
Replacement catalyst. Widely used in organic synthesis, the first metathesis catalyst; under a wide range of reaction conditions, it is effectively used in the tensioned ring-opening metathesis polymerization of end olefins, olefin cross-metathesis and ring-closing metathesis units and vinyl alcohol decomposition of internal olefin reaction.