Allylpalladium(II) chloride dimer
| Identification | ||
| Name |
|
Allylpalladium(II) chloride dimer |
| Synonyms |
|
chloropalladium(1+),prop-1-ene; |
|
|
||
| Molecular Structure |
|
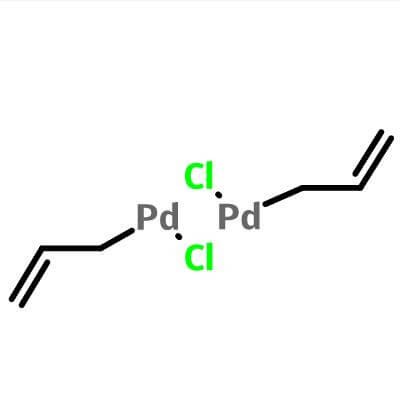 |
|
|
||
| Molecular Formula |
|
C6H10Cl2Pd2 |
| Molecular Weight |
|
365.89 |
| CAS Registry Number |
|
12012-95-2 |
| EINECS |
|
234-579-8 |
| Properties | ||
| Pd content |
|
58.2% up |
| Appearance |
|
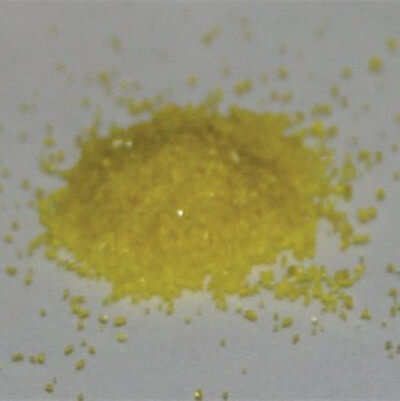
Yellow crystal |
|
Melting point |
|
120°C |
| Water solubility |
|
decomposes |
| Safety Data | ||
| Hazard Symbols |
|
Xi |
| Risk Codes |
|
R36/37/38 |
| Safety Description |
|
S26;S36 |
Allylpalladium(II) chloride dimer uses:
Used as a catalyst for homogeneous reactions and hydrosilylation.
1. A precatalyst for the enantioselective hydrosilylation of olefins.
2. Pre-catalyst for asymmetric alkylation and amination of cyclopropenyl acetate.
3. Cross-coupling reaction catalyst.
4. Dimers can be used as Trost ligands.
5. As a useful precursor for highly enantioselective allyl alkylation and amination.
6. Alkene stannous alkylation catalyst.
Allylpalladium(II) chloride dimer Advantage:
① Can control the single impurity content
② Purity can be controlled according to customer requirements
Used as a catalyst for the Heck reaction, and also as a catalyst to participate in the tandem nucleophilic allylation-alkoxyallylation reaction of alkynal with allyl chloride and allyl butylstannane.