| Identification | ||
| Name | 1,2,4-Triazole | |
| Synonyms | 1,2,4-1H-Triazole | |
|
|
||
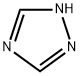
| Molecular Structure |
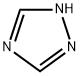
|
|
|
|
||
| Molecular Formula | C2H3N3 | |
| Molecular Weight | 69.07 | |
| CAS Registry Number | 288-88-0 | |
| EINECS | 206-022-9 | |
| Properties | ||
| Melting point | 119-122 ºC | |
| Boiling point | 260 ºC | |
|
density |
|
1.15 g/cm3 |
| Flash point | 140 ºC | |
|
form |
|
Crystalline Powder and Flakes |
| Water solubility | 1250 g/L (20 ºC) | |
| pka | 2.27(at 20℃) | |
|
refractive index |
|
1.4854 |
| Safety Data | ||
| Hazard Symbols | Xn | |
| Risk Codes | R22;R36;R63 | |
| Safety Description | S36/37 | |
1,2,4-triazole uses:
1,2,4-triazole is called triazole for short. It is an intermediate of triazole fungicides such as triadimefon, triadimefon, biphenyltriadimefon, tebuconazole, benzyl chlorotriadimefon, diniconazole, tetrazolitol, hexazonol, cyproconazole, propiconazole, flusilazole, trifluoconazole, furbendazole, oxazole, flurazole, oxymetazole, furfurazole, nitriconazole, furfurazole, and triazole plant growth regulators such as uniconazole and paclobutrazol.
1,2,4-triazole this product is used in the production of pesticides, pharmaceuticals (fluconazole), dyes, rubber additives, and also as a photoconductor for replication systems. Usage: Used as a pesticide and pharmaceutical intermediate, widely used in the synthesis of pesticides such as triadimefon, paclobutrazol, uniconazole, and conazole.




![2-[1,1-Biphenyl]-4-yl-4,6-Dichloro-1,3,5-Triazine,10202-45-6,C15H9Cl2N3](http://resourcewebsite.singoo.cc/14733039928352490/en/image/phone_5bbef823cd504.jpg)